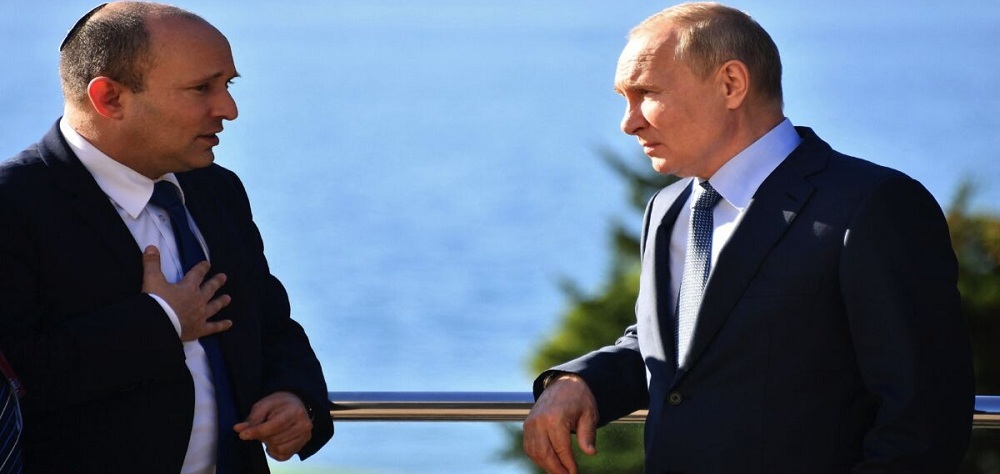
Alwaght- Russian President Vladimir Putin's recognition of independence of the self-proclaimed republics of Dontesk and Luhansk in eastern Ukraine on February 21 left the world divided between supporters and opponents of the move. A majority of the Western countries have condemned Putin's measure and threatened Moscow with major sanctions. They imposed them as Putin orders a military campaign in Ukraine on Thursday. Some countries close to Russia have welcomed the move. Meanwhile, one of the actors whose stance on the Ukrainian case can influence the future of its relations with Moscow and even its place in the security structure of West Asia is the Israeli regime.
Israeli procrastination regarding condemnation of Putin move and rise of dilemma of closeness to the West or friendship with Moscow
Despite the clear and quick reaction of many countries to the new decision of Putin on the crisis in Ukraine, evidence shows that the leaders of the Israeli regime have faced the case with procrastination and confusion. Israeli Foreign Minister Yair Lapid commented on the possibility of Tel Aviv joining the Western sanctions on Moscow, saying Israel would mull the measures it should take.
Also, the Hebrew-language Kan network recently revealed that there is a possibility of condemning Russia in connection with the conflict with Ukraine. The same network revealed that the Americans have not yet formally asked Israel to condemn Russia, but there are preparations for that. Leaders of the Democratic and Republican parties also told the channel that Israel was expected to issue a statement on the matter.
Now the Israeli regime's cabinet is facing historic decisions that could severely affect the future of Tel Aviv's relations with Moscow. On the one hand, Israeli officials are under pressure to reject, like Western countries, Putin's new decision on the two republics, Donetsk and Luhansk. It would mean that Tel Aviv would condemn Putin's decision and join Western sanctions against Russia. On the other hand, the Israelis, who have a significant volume of trade and close ties with Russia, are worried that they will end their close ties by taking anti-Russian positions and provoking Putin. In fact, declaring allegiance to the West or maintaining closeness with Russia is a dilemma in which the Israeli regime's political cabinet is drowning.
Worries about end of leeway to Israeli airstrikes on Syria
Undoubtedly, in the current situation, the most important concern of the Israelis in the Ukraine crisis is that Moscow will reconsider its appeasement-flavored security view to Tel Aviv and restrict their freedom of action in carrying out occasional airstrikes on Syrian army forces. Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov recently told his Syrian counterpart Faisal Meqdad at a meeting that "we strongly condemn Israeli attacks on Syria, which could escalate tensions in the region."
Lavrov's remarks must have been a clear message to the Israeli leadership in the midst of the Ukraine crisis, and this has greatly affected the security meeting of the Israeli cabinet. According to Kan network, during an Israeli cabinet's meeting on February 22 the Israelis went disappointed with the Russian condemnation of their anti-Syrian aggression and believed that Putin's anger could damage their freedom of military action in Syria.
Israeli-Russian unstable and unsuccessful friendship
Ukraine developments and the dubious Israeli reaction to Putin's recognition of two autonomous republics in eastern Ukraine is standing as a cause to suspicion on the friendly relations between Russia and Tel Aviv. Over the past years, the Israeli leaders have tried to paint Tel Aviv a close friend, and even an ally, to Moscow, and with this they sought privileges from Russia especially in Syria.
Since collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, relations between the two experienced a significant level of growth and closeness. The presence of Jews of Russian descent in the Israeli regime has undoubtedly played the most important role in the proximity of the two sides. Indeed, a population bridge involving more than a million Russians in the occupied Palestinian territories played an important role in expanding Moscow's relations with Tel Aviv, and even led to Vladimir Putin's visit to occupied Palestine in 2005. In response to show of passion by Russian-Israelis at Tel Aviv cultural center, Putin said he felt there was a small piece of Russian soil in Israel.
It is worth noting that the Russians run about 21 cultural and art institutions, publish several newspapers in Russian, and manage about 150 television channels and radio stations. Even over the past decades, a number of cabinet ministers in the Israeli regime have been from Russian roots, like Avigdor Lieberman, the leader of Yisrael Beiteinuand former foreign minister.
Trade between the two sides has grown significantly over the past three decades. Their trade volume which was $12 million in 1991 increased to about $2.8 billion in 2008 and to nearly $3.6 billion in 2015. Meanwhile, Russia's exports to the Israeli regime include mainly raw materials, including hydrocarbons, diamonds, wood and paper. Russia, along with Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan, is the main supplier of oil to the Israeli regime. Russia's imports are more diverse and include agricultural products, electronic wares, and medical services.
Also, one of the remarkable points is that the Israeli regime was the only player after France that was able to sell military weapons to Russia after the Second World War. Also, at the security, political and diplomatic level, there were close relations between the political officials of the two sides in recent years.
But despite all this positive trend, one issue has always been ignored and it is that Tel Aviv can never be outside the range of US-dominated major Western strategy.
In the current situation, the crisis in Ukraine has clearly shown that the issue of Israeli-Russian strategic alliance is more like an illusion that is far from the reality on the ground. Tel Aviv can not side with Moscow not only on the issue of Ukraine but also on any other crisis between Russia and the West because the existence and survival of this regime depends on submission to and cooperation with the West. The fact that a significant number of Jews of Russian descent live in the occupied Palestinian territories has not and will not guarantee a Tel Aviv-Moscow unity and alliance.
All these facts indicate that Putin should review his policy of closeness to Tel Aviv and patience with its aggressive policies in Syria and other regional crises and seek his allies, as Ukraine crisis showed, near the Russian borders. Even in terms of trade and economic interests, Moscow's relations with the Israeli regime have far less comparative advantages than trade with its neighbors. Now, thus, is safe to say that time has come for Moscow to review its policy concerning Tel Aviv.